Soil Mechanics
Soil type and moisture content are two major causes that can adversely affect the stability of a trench or excavation.
A number of stresses and deformations can occur in an open cut or trench. Among them are:
- tension cracks
- sliding, and
- toppling
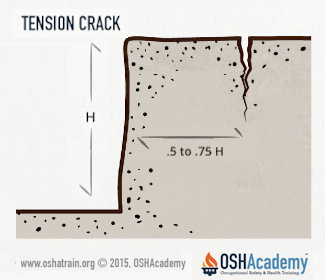
Tension Cracks
Soil always seeks its lowest level. In a deep trench, a horizontal force is exerted pushing the soil toward the trench. This can cause a tension crack to open on the surface of the ground at 0.5 to 0.75 times the trench depth (H) away from the top of the vertical face of the trench.
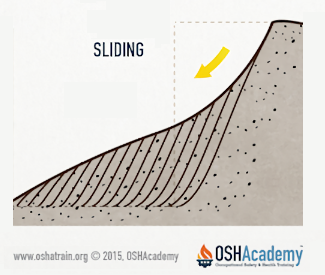
Sliding
Sliding or sluffing may occur as a result of soil slippage along the line of maximum stress. Of course, sliding will occur more often in loose previously-worked soils than in clay type soils.
Sliding is also much more common in after a heavy rain as the weight of the soil increases causing a layer of very moist soil on top of dryer layer similar to what happens in snow causing an avalanche. The tension crack allows the wet soil to slip causing a "landslide" of the trench wall similar to a large landslide along the sides of hills.
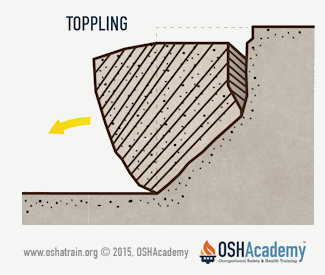
Toppling
Tension cracks can also cause toppling. Toppling occurs when the trench's vertical face shears along the tension crack line and topples into the excavation. This hazard is more common in loose soils that contain large rocks. For instance, you've all seen large rocks that have toppled down steep slopes to the road below.
Knowledge Check Choose the best answer for the question.
1-3. Tension cracks usually form at a horizontal distance of _____.
You forgot to answer the question!
