How Does the Ear Work?
The outer ear consists of the pinna, the ear canal, and the eardrum.
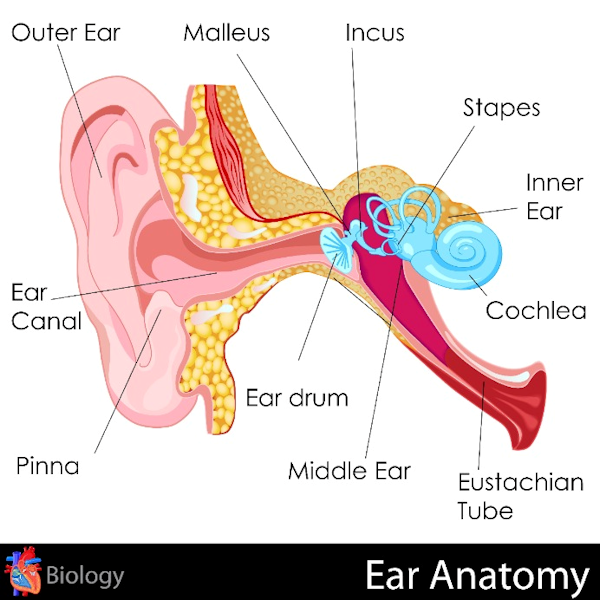
When sound waves enter the outer ear, the vibrations impact the ear drum and are transmitted to the middle and inner ear.
The middle ear consists of the ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes) and the ear drum. In the middle ear three small bones called the malleus (or hammer), the incus (or anvil), and the stapes (or stirrup) amplify and transmit the vibrations generated by the sound to the inner ear.
The inner ear consists of the cochlea and the auditory (hearing) nerve, which connect to the brain.The inner ear contains a snail-like structure called the cochlea which is filled with fluid and lined with cells with very fine hairs. These microscopic hairs move with the vibrations and convert the sound waves into nerve impulses - the result is the sound we hear. Exposure to loud noise can destroy these hair cells and cause hearing loss!
Knowledge Check Choose the best answer for the question.
1-2. In which part of the ear does injury occur due to excessive workplace noise?
You forgot to answer the question!
