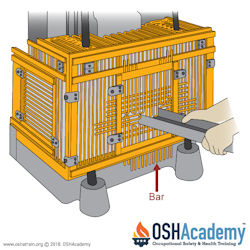
Point-of-Operation Guards
Point-of-operation machine guards are designed to prevent workers from inserting a body part into the operating machine.
The primary purpose of these guards is to prevent accidental contact with moving parts or other hazardous areas, reducing the risk of injuries like cuts, burns, or amputations.
They protect workers by enclosing or shielding dangerous machine parts. The number and complexity of machines and how they are used complicate machine guard design. For these reasons, not all machine manufacturers design effective point-of-operation guards on their products.
In many cases a point-of-operation guard can only be made and installed by the user after a thorough hazard analysis of the work requirements. In fact, poorly designed, built, or installed machine guards may create a hazard rather than eliminate one.
To be effective they must safeguard the employee while allowing the work to continue during normal operations with minimum disruption to the production process.
- Blade Guards: Metal or plastic barriers that cover the blades of saws or cutting machines, preventing access to sharp edges.
- Enclosure Guards: Rigid guards that completely enclose moving parts such as gears, belts, and chains, keeping them inaccessible during operation.
- Barrier Guards: Fixed guards placed around hazardous areas of machines like conveyors or rotating shafts, preventing workers from reaching dangerous parts.
- Fan Guards: Covers placed over industrial fans to prevent fingers, clothing, or other objects from coming into contact with the blades.
- Perimeter Guards: Fencing or barriers installed around large machines like robots or presses, preventing workers from entering hazardous areas.
- Fixed Covers: Non-removable covers placed over openings in machines, such as flywheels or rotating drums, to prevent accidental contact.
Knowledge Check Choose the best answer for the question.
5-3. Which type of machine safeguard is designed to prevent workers from inserting a body part into an operating machine?
You forgot to answer the question!