Radiation
Ionizing and Non-Ionizing Radiation
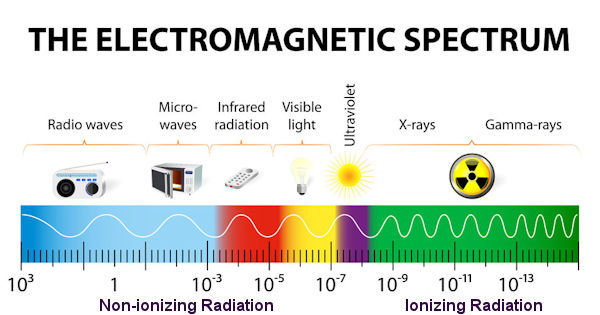
Radiation includes a wide range of energies forming the electromagnetic spectrum, which is illustrated to the right.
The energy of the radiation shown on the spectrum to the right increases from left to right as the frequency rises. The spectrum has two major divisions:
- Non-ionizing radiation: Radiation that has enough energy to move atoms in a molecule around or cause them to vibrate, but not enough to remove electrons, is referred to as "non-ionizing radiation." Examples of this kind of radiation are radio waves, visible light, and microwaves.
- Ionizing radiation: Radiation that falls within the ionizing radiation range has enough energy to remove tightly bound electrons from atoms, thus creating ions. This is the type of radiation that people usually think of as 'radiation.' We take advantage of its properties to generate electric (nuclear) power, to kill cancer cells, and in many manufacturing processes.
Time, Distance, and Shielding
Time, distance, and shielding actions minimize your exposure to radiation in much the same way as they would to protect you against overexposure to the sun:
- Time: For people who are exposed to radiation in addition to natural background radiation, limiting or minimizing the exposure time reduces the dose from the radiation source.
- Distance: Just as the heat from a fire reduces as you move further away, the dose of radiation decreases dramatically as you increase your distance from the source.
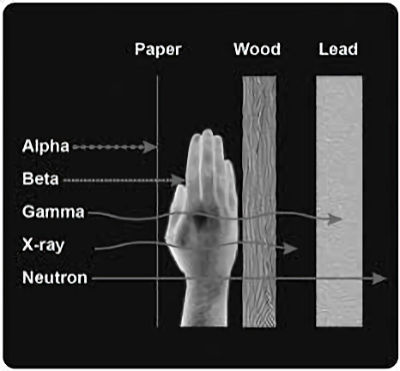
- Shielding: Barriers of lead, concrete, or water provide protection from penetrating gamma rays and x-rays. This is why certain radioactive materials are stored under water or in concrete or lead-lined rooms, and why dentists place a lead blanket on patients receiving x-rays of their teeth. Therefore, inserting the proper shield between you and a radiation source will greatly reduce or eliminate the dose you receive.
Knowledge Check Choose the best answer for the question.
2-5. Lead shielding is used by dentists to protect against _____.
You forgot to answer the question!