05.B Eye and Face Protection.
05.B.01
Persons must be provided with eye and face protection for the specific jobsite hazards, as listed in Table 5-1, when machines or operations present potential eye or face injury.
- Eye and face protection must meet the requirements of ANSI/American Society of Safety Engineers (ASSE) Z87.1 , and bear a legible and permanent "Z87" logo to indicate compliance with the standard.
- Eye and face protection must be distinctly marked to identify manufacturer.
Table 5-1
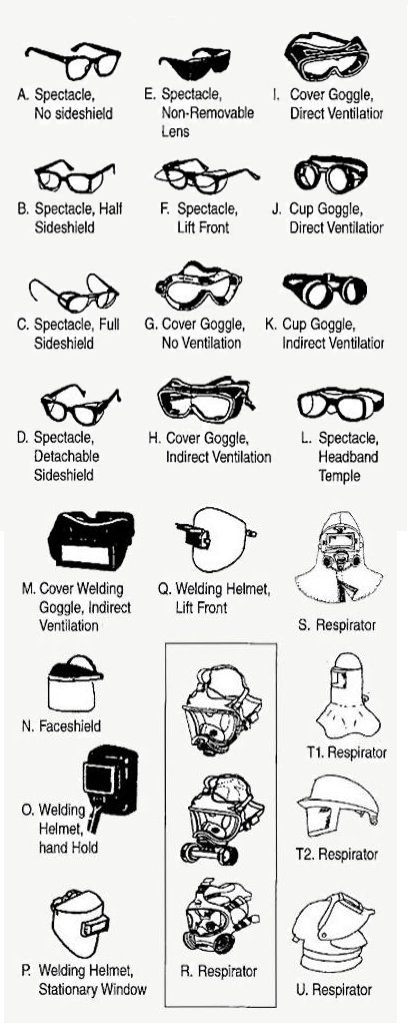


Table 5-1 (Continued)
| IMPACT: Chipping, grinding, machining, masonry work, riveting and sanding | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assessment See Note (1) |
Protector Type | Protectors | Limitations | Not Recommended |
| Flying fragments, objects, large chips, particles, sand, dirt, etc. | B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, N | Spectacles, goggles, faceshields See Notes (1)(3)(5)(6) (10) For severe exposures: add N |
Protective devices do not provide unlimited protection. See Note (7) | Protectors that do not provide protection from side exposure
See Note (10) Filter or tinted lenses that restrict light transmittance, unless it is determined that a glare hazard exists. Refer to Optical Radiation |
| HEAT: Furnace operations, pouring, casting, hot dipping, gas cutting, and welding | ||||
| Hot sparks | B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, N | Faceshields, goggles, spectacles For severe exposure,add N See Notes (2)(3) |
Spectacles, cup and cover-type goggles do not provide unlimited facial protection See Note (2) |
Protectors that do not provide protection from side exposure |
| Splash from Molten Metals | N | Faceshields worn over goggles H,K See Notes (2)(3) |
||
| High Temperature Exposure | N | Screen faceshields, reflective faceshields | See Note (3) | |
| CHEMICAL: Acid and chemical handling, degreasing, plating | ||||
| Splash | G, H, K N | For severe exposure add N | Ventilation should be adequate but protected from splash entry | Spectacles, welding helmets, hand shields |
| Irritating mists | G | Special purpose goggles | See Note (3) | |
| DUST: Woodworking, buffing, general industry conditions | ||||
| Nuisance dust | G, H, K | Goggles, eyecup and cover types | Atmospheric conditions and the restricted ventilation of the protector can cause lenses to fog. Frequent cleaning may be required. |
|
| OPTICAL RADIATION: Welding: electric arc | ||||
| O, P, Q | Typical filter lens shade | Protection from optical radiation is directly related to filter lens density. See Note (4). Select the darkest shade that allows adequate task performance |
Protectors that do not provide protection from optical radiation. | |
NOTES:
- Care should be taken to recognize the possibility of multiple and simultaneous exposure to a variety of hazards. Adequate protection against the highest level of each of the hazards must be provided.
- Operations involving heat may also involve optical radiation. Protection from both hazards shall be provided.
- Faceshields shall only be worn over primary eye protection.
- Filter lenses shall meet the requirements for shade designations in Table 5-2.
- Persons whose vision requires the use of prescription (Rx) lenses shall wear either protective devices fitted with prescription (Rx) lenses with sideshields or protective devices designed to be worn over regular prescription (Rx) eyewear.
- Wearers of contact lenses shall also be required to wear appropriate covering eye and face protection devices in a hazardous environment. It should be recognized that dusty and/or chemical environments may represent an additional hazard to contact lens wearers.
- Caution should be exercised in the use of metal frame protective devices in electrical hazard areas.
- Refer to ANSI/ASSE Z87-1, Section 6.5, Special Purpose Lenses.
- Welding helmets or hand shields shall be used only over primary eye protection.
- Non-sideshield spectacles are available for frontal protection only.
05.B.02
When eye protection is required by this regulation, persons whose vision requires the use of corrective lenses, whether via the use of contact lenses or eyeglasses, must be protected by one of the following:
- Prescription safety glasses providing optical correction and equivalent protection;
- Protective glasses with sideshields designed to fit over corrective lenses without disturbing the adjustment of the glasses;
- Goggles that can be worn over corrective lenses without disturbing the adjustment of the glasses, or
- Goggles that incorporate corrective lenses mounted behind the protective lenses.
05.B.03
Personnel who are considered blind in one eye and are working in other than administrative functions must wear safety glasses with sideshields at all times.
05.B.04
Operations that require the use of, or exposure to, hot or molten substances (e.g., babbitting, soldering, pouring or casting of hot metals, handling of hot tar, oils, liquids, and molten substances) must require eye protection, such as goggles with safety lenses and screens for side protection, or face masks, shields, and helmets giving equal protection. Lens mountings must be able to retain in position all parts of a cracked lens.
05.B.05
Operations that require handling of harmful materials (e.g., acids, caustics, hot liquids, or creosoted materials) and operations where protection from gases, fumes, and liquids is necessary, must require the wearing of goggles with cups of soft pliable rubber and suitable faceshields, masks, or hoods that cover the head and neck, and other protective clothing appropriate to the hazards involved.
05.B.06
Operations where protection from radiant energy with moderate reduction of visible light is necessary, including welding, cutting, brazing, and soldering, must require eye and face protection suitable to the type of work, providing protection from all angles of direct exposure, and with lenses of the appropriate shade. > See Table 5.2.
| OPERATION | SHADE NUMBER |
|---|---|
| Soldering | 2 |
| Torch Brazing | 3 or 4 |
| Cutting (light) up to 1 in (2.5 cm) | 3 or 4 |
| Cutting (medium) 1 to 6 in (2.5 to 15.2 cm) | 4 or 5 |
| Cutting (heavy) 6 in (15.2 cm) or more | 5 or 6 |
| Gas welding (light) up to 1/8 in (0.3 cm) | 4 or 5 |
| Gas welding (medium) 1/8 to 1/2 in (0.3 to 1.2 cm) | 5 or 6 |
| Gas welding (heavy) 1/2 in (1.2 cm) or more | 6 or 8 |
| Atomic hydrogen welding | 10 – 14 |
|
Inert-gas metal-arc welding (nonferrous): 1/16 in to 5/32 in (0.1 to 0.4 cm) electrodes |
11 |
|
Inert-gas metal-arc welding (ferrous) - 1/16 to 5/32 in (0.1 to 0.4 cm) electrodes |
12 |
| Shielded metal-arc welding - 1/16 to 5/32 in (0.1 to 0.4 cm) electrodes | 10 |
| Shielded metal-arc welding - 3/16 to 1/4 in (0.4 to 0.6 cm) electrodes | 12 |
| Shielded metal-arc welding - 5/16 to 3/8 in (0.7 to 0.9 cm) electrodes | 14 |
| Carbon arc welding | 14 |
| Plasma arc cutting up to 100 amps | 8 |
| Plasma arc cutting 100 to 200 amps | 10 |
| Plasma arc cutting 200 to 400 amps | 12 |
| Plasma arc cutting greater than 400 amps | 14 |
05.B.07
Glare-resistant glasses that comply with ANSI Z80.3 with an ultraviolet A-region (UVA) and ultraviolet B-region (UVB) 99% filtration must be worn when conditions require protection against glare. When conditions so warrant, polarized lenses must also be considered.
05.B.08
Tinted or automatically darkening lenses should not be worn when work tasks require the employee to pass often from brightly to dimly lighted areas.
Knowledge Check Choose the best answer for the question.
5-3. How does eye and face protection equipment indicate compliance with required standards?
You forgot to answer the question!
