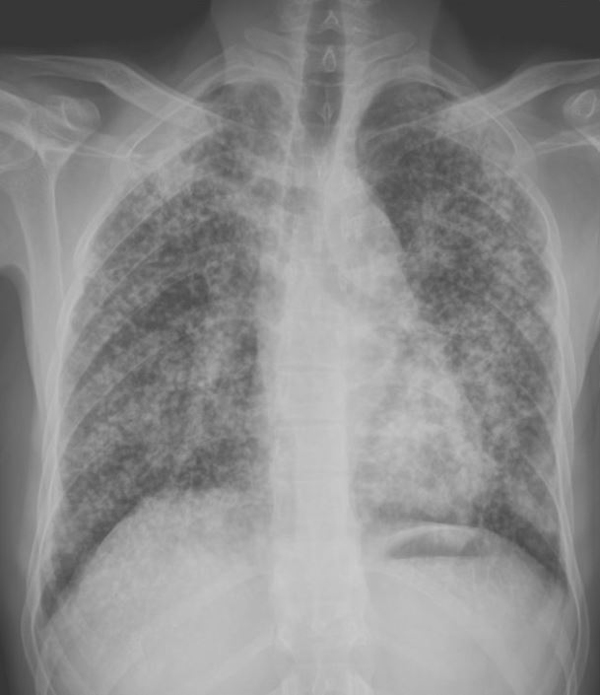
Silicosis
Silicosis is a disabling and incurable lung disease, and can be diagnosed in dental laboratory workers. However, it is preventable. Silicosis is caused by breathing in fine dust containing crystalline silica. Once in the lungs, this dust then causes damage that stops the body from using oxygen properly. Breathing in dust containing silica has been linked to other diseases, such as tuberculosis, kidney disease, and lung cancer.
Symptoms include:
- shortness of breath
- severe cough
- wheezing
- chest tightness
Dental labs materials that contain silica:
- sand
- investment materials
- porcelain
- shop dust
Controlling Silica Exposure
The best method to stop silica exposure is to eliminate materials containing crystalline silica. However, this method is not feasible for sandblasting machines. In this case, aluminum oxide is one of the many acceptable substitutions to silica.
When there are no good substitutes, dust exposure should be minimized through the use of local exhaust ventilation systems. These systems capture dust and transport it to a dust collection system.
The worker should also wear a respirator when other control methods are not available or do not work properly. The type of respirator recommended is, at a minimum, a half-mask air-purifying respirator with type N-100 particulate filters.
Wet wiping, wet moping, and vacuuming with a HEPA vacuum are also recommended. Dry sweeping, dry dusting, use of compressed air, and use of ordinary vacuum cleaners should be avoided because they reintroduce the dust into the air.
Knowledge Check Choose the best answer for the question.
1-2. Breathing in dust containing silica has been linked to other diseases, such as _______.
You forgot to answer the question!