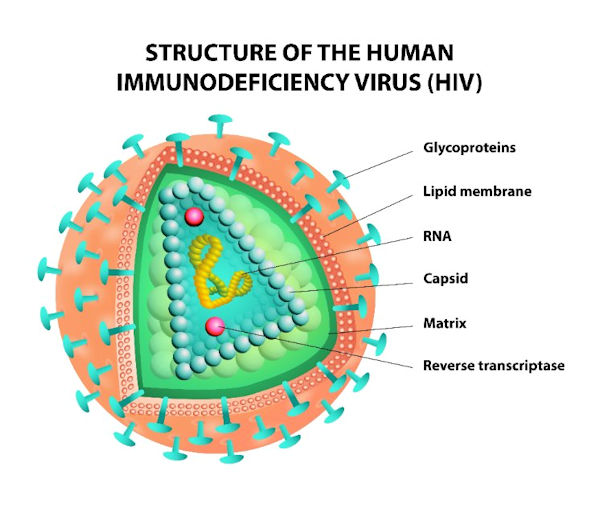
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
It can take many years before an HIV-infected person displays symptoms of the disease.
Symptoms include:
- enlarged lymph nodes
- fatigue
- frequent fevers
- persistent or frequent yeast infections of the mouth or vagina
- persistent or frequent skin rashes
- short-term memory loss
- weight loss
- enlarged liver and spleen
As with hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus, it is important to understand individuals with HIV are potentially infectious to others, even though they may have no observable symptoms.
Presently, there is no known cure for HIV. Treatment for HIV is called antiretroviral therapy or ART. If people with HIV take ART as prescribed, their viral load (amount of HIV in their blood) can become undetectable. If it stays undetectable, they can live long, healthy lives. Today, someone diagnosed with HIV and treated before the disease is far advanced can live nearly as long as someone who does not have HIV.
HIV cannot reproduce outside the human body. It is not spread by:
- air or water
- insects, including mosquitoes: studies conducted by CDC researchers and others have shown no evidence of HIV transmission from insects
- saliva, tears, or sweat. There is no documented case of HIV being transmitted by spitting
- casual contact like shaking hands or sharing dishes.
- closed-mouth or "social" kissing
All reported cases suggesting new or potentially unknown routes of transmission are thoroughly investigated by state and local health departments with assistance, guidance, and laboratory support from CDC.
Disease Comparison
Of the three major bloodborne pathogens, hepatitis B virus is the most contagious. Approximately 33% of individuals exposed to Hepatitis B virus will become infected. Of those individuals exposed to Hepatitis C virus, only about 2% will become infected. Comparatively, human immunodeficiency virus is much less contagious than either form of hepatitis. About 0.33%, or 1 in 300, people exposed to HIV will become infected with the virus. Despite these statistics, every exposure has the potential to transmit bloodborne pathogens and must be considered significant.
Knowledge Check Choose the best answer for the question.
2-10. Which of the three major bloodborne pathogens is the most contagious, with approximately 33% of those exposed becoming infected?
You forgot to answer the question!