Oxygen Deficiency
The normal atmosphere is composed approximately of 20.9% oxygen, 78.1% nitrogen, and 1% argon with small amounts of various other gases.
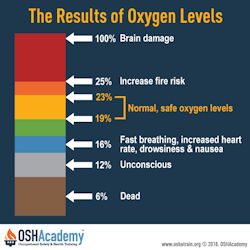
Oxygen levels below 19% is considered deficient and dangerous. Important points to know about hazardous atmospheres include:
- Oxygen deprivation is one form of asphyxiation. While it is desirable to maintain the atmospheric oxygen level at 21% by volume, the body can tolerate deviation from this ideal.
- When the oxygen level falls to 17%, the first sign of hypoxia is a deterioration of night vision which is not noticeable until a normal oxygen concentration is restored. The physiologic effects are increased breathing volume and accelerated heartbeat.
- Between 14-16%, the physiologic effects are increased breathing volume, accelerated heartbeat, very poor muscular coordination, rapid fatigue, and intermittent respiration.
- Between 6-10%, the effects are nausea, vomiting, inability to perform, and unconsciousness.
- Less than 6%, spasmodic breathing, convulsive movements, and death in minutes.
How Does Oxygen Become Deficient?
Reduction of oxygen in a confined space may be the result of either consumption or displacement.
- Oxygen consumption: The consumption of oxygen takes place during combustion of flammable substances, as in welding, heating, cutting, and brazing. A subtler consumption of oxygen occurs during bacterial action, as in the fermentation process. Oxygen may also be consumed during chemical reactions as in the formation of rust on the exposed surface of the confined space (iron oxide). The number of people working in a confined space and the amount of their physical activity will also influence the oxygen consumption rate.
- Oxygen displacement: Oxygen becomes deficient if it is displaced by another gas. Examples of gases that are used to displace air, and therefore reduce the oxygen level, are helium, argon, and nitrogen. Carbon dioxide may also be used to displace air and can occur naturally in sewers, storage bins, wells, tunnels, wine vats, and grain elevators.
Certain gases are also used as inerting agents to displace flammable substances and retard pyrophoric reactions. Gases such as nitrogen, argon, helium, and carbon dioxide, are frequently referred to as non-toxic, inert gases but have claimed many lives. In fact, the use of nitrogen to inert a confined space has claimed more lives than carbon dioxide.
- The total displacement of oxygen by nitrogen will cause immediate collapse and death.
- Carbon dioxide and argon, with specific gravities greater than air, may lie in a tank or manhole for hours or days after opening.
Since these gases are colorless and odorless, they pose an immediate hazard to health unless appropriate oxygen measurements and ventilation are carried out.
Knowledge Check Choose the best answer for the question.
2-3. Because carbon dioxide has a specific gravity greater than air, it can _____ oxygen in a tank for hours or days after opening.
You forgot to answer the question!