Current
The amount of internal current a person can withstand and still be able to control the muscles of the arm and hand can be less than 10 milliamperes (milliamps or mA).
Entrance Wound

Currents above 10 mA can paralyze or "freeze" muscles. When this "freezing" happens, a person is no longer able to release a tool, wire, or other object. In fact, the electrified object may be held even more tightly, resulting in longer exposure to the shocking current. For this reason, hand-held tools that give a shock can be very dangerous.
If you can't let go of the tool, current continues through your body for a longer time, which can lead to respiratory paralysis (the muscles that control breathing cannot move). You stop breathing for a period of time.
Exit Wound
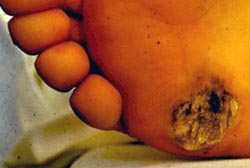
People have stopped breathing when shocked with currents from voltages as low as 49 volts. Usually, it takes about 30 mA of current to cause respiratory paralysis.
Currents greater than 75 mA may cause ventricular fibrillation (very rapid, ineffective heartbeat). This condition will cause death within a few minutes unless a special device called a defibrillator is used to save the victim.
Heart paralysis occurs at 4 amps, which means the heart does not pump at all. Tissue is burned with currents greater than 5 amps.
Knowledge Check Choose the best answer for the question.
2-4. What level of electrical current may cause muscles to be paralyzed or "freeze" so that the employee is unable to release a tool, wire, or object when contacted?
You forgot to answer the question!
