Identify and Analyze Fall Hazards
We know that eliminating all fall hazards on the construction site is impossible because they are inherent in the nature of construction work.
However, it is possible to mitigate (to become less harmful) many hazards for tasks that must be performed at elevation. To begin the process, identify each worksite fall hazard and analyze each one for the following variables that help to determine the risk that a hazard presents:
- Probability – the likelihood of a fall accident if the employee is exposed to a hazard; and
- Severity – the magnitude of the injury ranging from no injury to fatal injury;
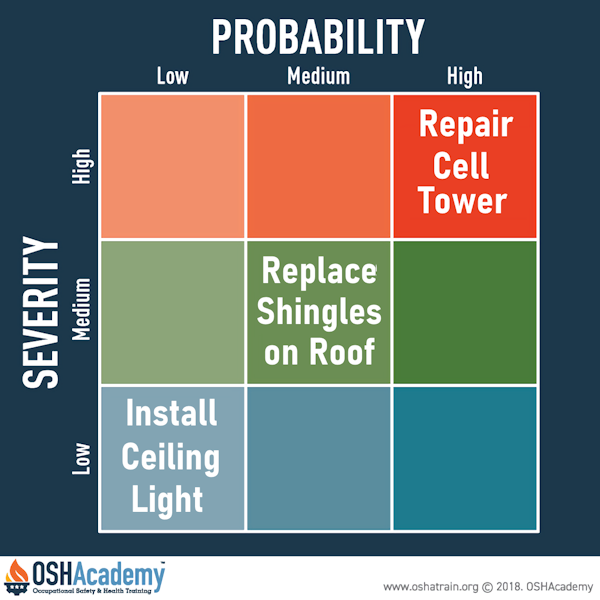
You can use a risk matrix to help you determine the degree of risk different worksite task might present. Know that will help you determine appropriate fall-protection systems for your worksite.
Many factors affect the probability of a fall accident and the severity of injury.
- Scope – the number of employees performing a task
- Frequency – how frequently the task will be performed
- Rapidity – how quickly an employee must perform a task
- Duration – how long it takes an employee to perform a task
- Elevation – the height at which an employee will perform a task
- Orientation – the body part(s) that will likely strike a lower surface
- Equipment – exposure to sharp points, moving parts, and hazardous energy
- Materials – exposure to toxic chemicals, substances, and materials
- Exertion – the demand on an employee to exert excessive force (lifting, lowering, pushing, or pulling)
- Physical environment – workplace temperature, atmospheres, humidity, illumination, and noise
- Psychosocial environment – the psychological stress that causes distraction
- Response – the promptness of rescue and quality of treatment of an injury
- What is the fall distance from the walking/working surface to the next lower level?
- How many workers are exposed to the hazard?
- What tasks and work areas are associated with the hazard?
- How will the workers move - horizontally, vertically, or in both directions - to do their tasks?
- Are secure anchorages available or can they be easily installed near the hazard?
- Are there other hazards near the work area, such as overhead power lines?
- How will workers be promptly rescued if they are suspended in a personal fall-arrest system?
Knowledge Check Choose the best answer for the question.
5-2. What are the two primary variables that help determine the risk that a hazard presents?
You forgot to answer the question!