Robot Systems
Types of Robot Hazards
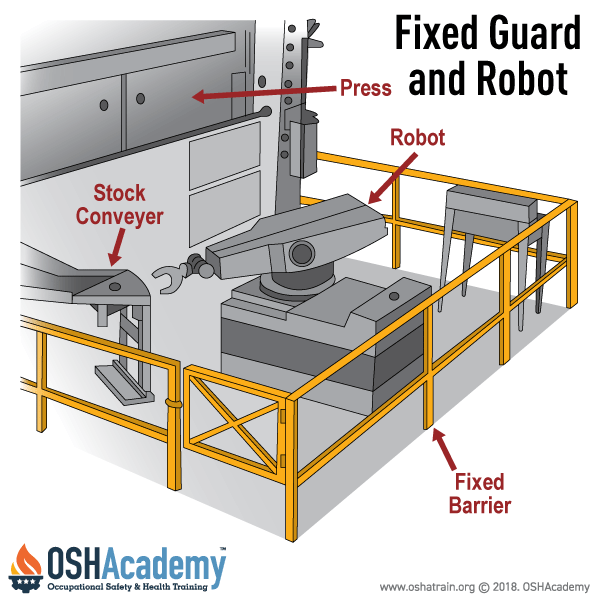
The use of robotics in the workplace can also present potential mechanical and human hazards.
Mechanical hazards could involve workers colliding with equipment, getting crushed or trapped by machinery, or sustaining injuries from falling equipment parts. For instance, a worker might collide with the robot's arm or peripheral equipment due to unexpected movements, component malfunctions, or unforeseen program changes.
A worker could be harmed by being caught between the robot's arm and other peripheral equipment, or being crushed by peripheral equipment due to the robot's impact on this equipment. Mechanical hazards can also arise from the mechanical failure of components related to the robot or its power source, drive components, tooling or end-effector, and/or peripheral equipment. Failures of gripper mechanisms that result in parts being released, or failures of end-effector power tools like grinding wheels, buffing wheels, deburring tools, power screwdrivers, and nut runners, to name a few, can contribute to these hazards.
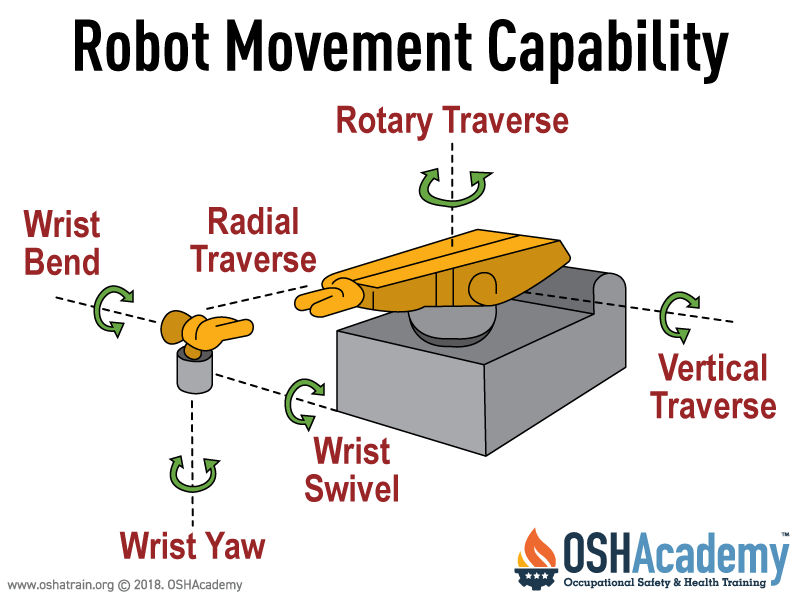
Human errors can lead to hazards for both personnel and equipment. Mistakes in programming, interfacing peripheral equipment, and connecting input/output sensors can lead to unexpected movements or actions by the robot, which in turn can lead to personnel injuries or equipment damage.
Frequent errors in human judgment often stem from incorrectly activating the teach pendant or control panel. The most significant judgment error arises from becoming overly familiar with the robot's redundant motions, causing personnel to be too trusting in assuming the nature of these motions and thus placing themselves in hazardous positions while programming or performing maintenance within the robot's work envelope.
Knowledge Check Choose the best answer for the question.
4.5 What is the most significant human judgment error when working around robots?
You forgot to answer the question!