Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA)
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus is a common multi-drug-resistant bacterium that causes staph infections (MRSA) in different parts of the body.
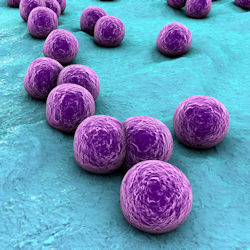
It is carried by about 2‰ of the population in the U.S. with nearly 19,000 infections resulting in sepsis causing death.
Staph infections are common among the general population, and since the 1970s, there has been a dramatic increase in infections caused by MRSA in hospitals and clinics, nursing homes, laboratories, and housekeeping, and is becoming more common in locker rooms and laundry facilities. The MRSA bacterium has become resistant to many antibiotics and is now considered a "superbug."
MRSA can cause severe problems including:
- bloodstream infections
- pneumonia
- skin/injury site infections
- sepsis
- death
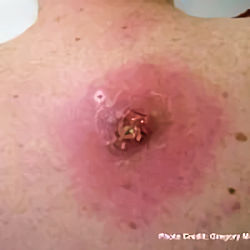
Preventing the Spread of MRSA
- Cover your wounds with clean, dry bandages until healed.
- Follow your healthcare provider's instructions about proper care of the wound. Pus from infected wounds can contain MRSA.
- Do not pick at or pop the sore.
- Throw away bandages and tape with the regular trash.
- Clean your hands often. Wash hands often with soap and water or use an alcohol-based hand rub, especially:
- after changing a bandage
- after touching an infected wound
- after touching dirty clothes
Knowledge Check Choose the best answer for the question.
2-10. Which of the following bloodborne pathogens has become drug-resistant and is considered a "superbug?"
You forgot to answer the question!
