Hepatitis C Virus (HCV)
The hepatitis C virus (HCV) is also a significant cause of severe liver damage and death.
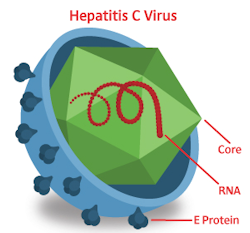
In 2020, there were 4,295 reported cases of acute hepatitis C, which corresponds to a rate of 1.3 cases per 100,000 population.
About 3.5 million Americans are currently living with hepatitis C and roughly half are unaware of their infection. Approximately 1 to 5% of people infected with hepatitis C virus die as a result of the long-term damage caused to the liver and body.
Approximately 70%-80% of people with acute hepatitis C do not have any symptoms. Some people, however, can have mild to severe symptoms soon after being infected, including:
- fever
- fatigue
- loss of appetite
- nausea
- vomiting
- abdominal pain
- dark urine
- grey-colored bowel movements
- joint pain
- jaundice (yellow color in the skin or eyes)
Click here to view the CDC fact sheet for Hepatitis C. (PDF)
Knowledge Check Choose the best answer for the question.
2-5. Approximately how many people infected with the hepatitis C virus die as a result of the long-term damage caused to the liver and body?
You forgot to answer the question!
