Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)
The hepatitis B virus (HBV) is one of the primary causes of Hepatitis, an infection which causes inflammation of the liver.
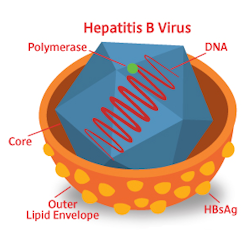
Complications of Hepatitis include cirrhosis (scarring) of the liver, liver cancer, and liver failure. There is no known cure for the hepatitis B virus. In the United States, approximately 15 to 25 percent of people infected with HBV will die because of the illness.
Hepatitis B can be either acute or chronic.
- Acute hepatitis B virus infection is a short-term illness that occurs within the first 6 months after someone is exposed to the hepatitis B virus. Acute infection can, but does not always, lead to chronic infection.
- Chronic hepatitis B virus infection is a long-term illness that occurs when the Hepatitis B virus remains in a person's body. Chronic hepatitis B is a serious disease that can result in long-term health problems, and even death.
In 2020, a total of 2,964 cases of acute hepatitis B were reported to the CDC, which corresponds to a rate of 0.9 cases per 100,000 population. This represents a decrease from the 3,192 reported cases in 2019.
However, it is important to note that the actual number of acute hepatitis B cases is believed to be much higher than the reported cases. According to the CDC, the estimated number of acute hepatitis B cases in 2020 was almost 20,000.
Knowledge Check Choose the best answer for the question.
2-2. The hepatitis B virus causes an inflammation and possibly cirrhosis of the _____.
You forgot to answer the question!
